Brazil’s Supreme Court resumed hearings Wednesday in a closely watched case on whether to restrict native peoples’ rights to claim their ancestral lands, a key buffer against climate change.
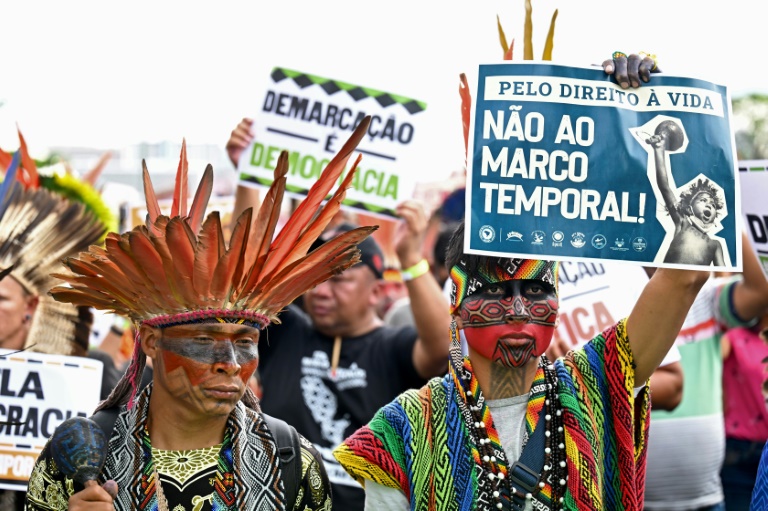
Hundreds of Indigenous protesters, many in traditional feather headdresses, rallied in the capital Brasilia as the court weighed the legality of the so-called “time-frame argument,” which holds that native peoples should not have the right to lands where they were not present in 1988, when the current constitution was ratified.
Indigenous groups say that violates their rights, given that many were forced from their ancestral lands, including during the military dictatorship that ruled Brazil from the 1960s to 1980s.
The Supreme Court began hearing the case in 2021, but has adjourned the proceedings several times.
So far, two of the court’s 11 justices have sided with the Indigenous plaintiffs, and two against them, one of these a judge who announced his stance on Wednesday.
Climate campaigners have joined Indigenous activists in pressing for the court to reject the time-frame argument, given that numerous studies have found that protected Indigenous reservations are one of the best ways to fight deforestation and, with it, global warming.
“The argument ignores our constitutional rights to our ancestral lands, puts existing Indigenous reservations at risk and makes creating new ones unviable,” Dinamam Tuxa, coordinator of the Association of Brazil’s Indigenous Peoples (APIB), told AFP ahead of the trial.
Indigenous rights groups have dubbed the case the “trial of the century.”
The UN High Commissioner for Human Rights said in a statement that a win for the time-frame limitation argument would be “a big setback” for the rights of Indigenous people in Brazil and go against international human rights norms.
The limitation is backed by Brazil’s powerful agribusiness lobby, which scored a victory in May when the lower house of Congress passed a bill enshrining the 1988 cutoff in law.
The bill is now working its way through the Senate.
Leftist President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva, a self-described ally of Indigenous peoples, is expected to veto the bill if it passes. But Congress, where the agribusiness coalition is a major player, could override a veto.
The case could enter murky legal territory if that happens before the Supreme Court’s justices finish delivering their rulings.
The constitution makes no mention of a cutoff date in relation to Indigenous reservations.
Indigenous reservations cover 11.6 percent of Brazil’s territory, notably in the Amazon rainforest.
Brazil has around 1.7 million Indigenous inhabitants — 0.8 percent of the population.