AFP
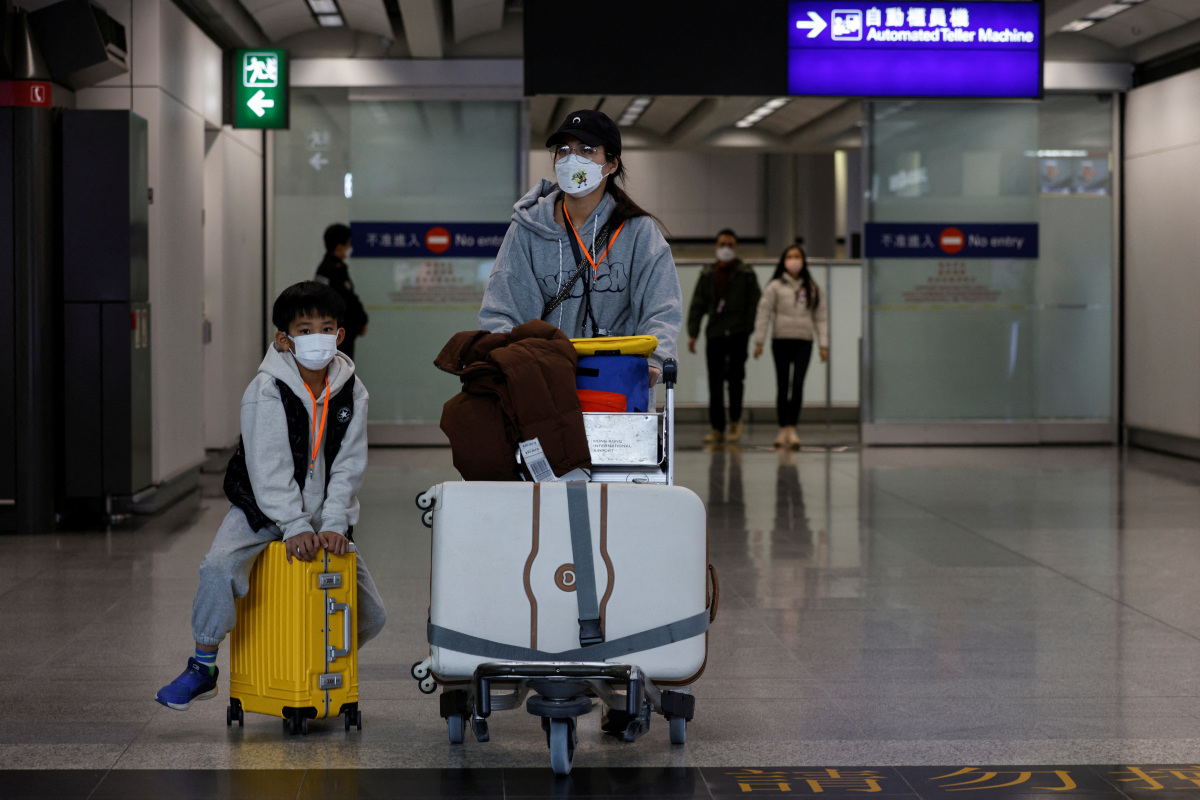
Beijing’s sudden pivot away from containing Covid-19 has caused jitters around the world, with the United States saying it may restrict travel from China following its decision to end mandatory quarantine for overseas arrivals.
China late Monday scrapped quarantine for inbound travellers from January 8 onwards, dismantling the last remaining piece of its stringent zero-Covid policy and ending some of the world’s harshest border restrictions.
The move was greeted with jubilation by Chinese citizens, who rushed to book international flights, triggering a surge in ticket prices.
But other countries have expressed concerns about the potential for new variants as China battles the world’s biggest surge in infections.
US officials said late Tuesday they were considering Covid entry restrictions on travellers from China, after countries including Japan and India introduced PCR testing on arrival for Chinese passengers.
“There are mounting concerns in the international community on the ongoing Covid-19 surges in China and the lack of transparent data, including viral genomic sequence data, being reported from the PRC,” the US officials said, referring to the People’s Republic of China.
The United States is “considering taking similar steps” to countries such as Japan and Malaysia, they added.
Taiwan, a self-ruled island that China claims as its own, said Wednesday that it would also screen travellers from the mainland for the virus.
China’s loosening of measures effectively brought the curtain down on a zero-Covid regime of mass testing, lockdowns and long quarantines that has roiled supply chains and buffeted business engagement with the world’s second-largest economy.
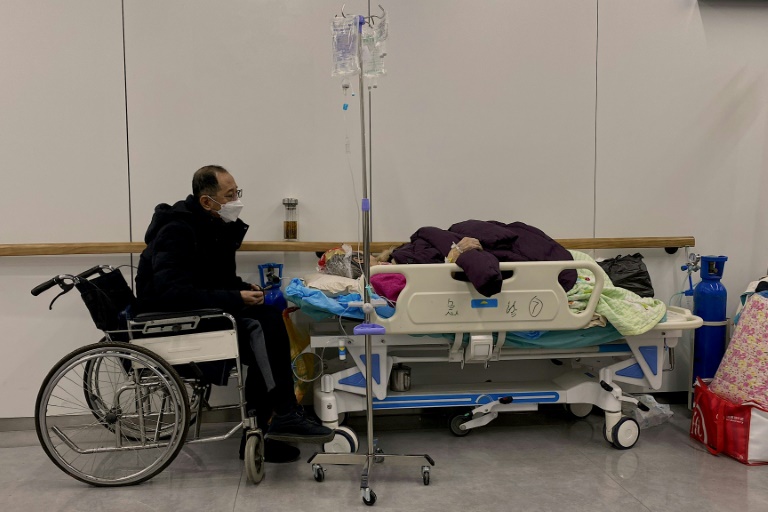
Hospitals and crematoriums across China have been overwhelmed with undervaccinated elderly patients, while residents report widespread shortages of fever medicine as the virus spreads largely unchecked among the population of 1.4 billion.
Asked about Japan’s entry restrictions, Beijing’s foreign ministry Tuesday said that countries should uphold “scientific and appropriate” disease controls that “should not affect normal personnel exchanges”.
All passengers arriving in China have had to undergo mandatory centralised quarantine since March 2020. The period of isolation fell from three weeks to one week in June, and to five days last month.
The end of that rule in January will also see Covid-19 downgraded to a Class B infectious disease, allowing authorities to adopt looser controls.
On Tuesday, Chinese immigration authorities announced the gradual resumption from January 8 of passport issuance for “tourism” or “overseas visits of friends”.
The winter surge comes ahead of major public holidays next month in which hundreds of millions of people are expected to travel to their hometowns to reunite with relatives.
Chinese authorities have admitted the scale of the outbreak is now “impossible” to track and narrowed the criteria for defining Covid deaths.
China’s Center for Disease Prevention and Control reported 5,231 new Covid cases and three deaths nationwide Wednesday — likely a drastic undercount since people are no longer required to declare infections to authorities.
Authorities are using data from online surveys, hospital visits, demand for fever medicines and emergency calls to “make up for shortcomings in (officially) reported figures”, disease control official Yin Wenwu said at a press briefing Tuesday.
And as the country faces shortages of basic medicines, Beijing city authorities plan to distribute the oral Covid drug Paxlovid at local hospitals and community clinics, but it remains extremely difficult to obtain for ordinary people.
The US-developed treatment was briefly available on e-commerce platform JD.com and delivery platform Meituan in the past few days before both ran out of stock.