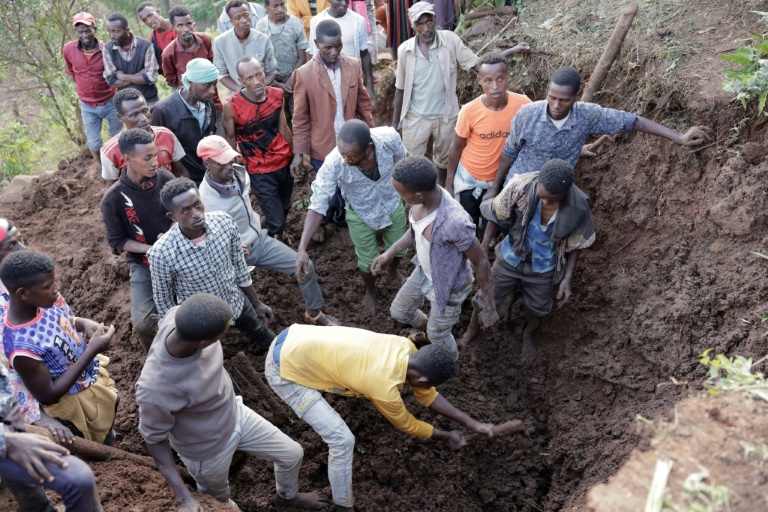
The death toll from landslides in a remote region of southern Ethiopia has risen to 257, the United Nations said Thursday, warning that the number of victims could soar to up to 500.
Rescuers are pressing on with the grim search for bodies and survivors in the stricken locality of Kencho Shacha Gozdi, with crowds of distraught locals digging through a sea of mud often using just their bare hands and shovels.
“The death toll has risen to 257,” as of July 24, the UN’s humanitarian agency OCHA said in statement citing local authorities. “The death toll is expected to rise to up to 500 people.”
OCHA said more than 15,000 people need to be evacuated because of the high risk of further landslides, including at least 1,320 children under the age of five and 5,293 pregnant women or new mothers.
Aid has begun arriving in the isolated, hard-to-reach area, including four trucks of life-saving supplies from the Ethiopian Red Cross Society, it said.
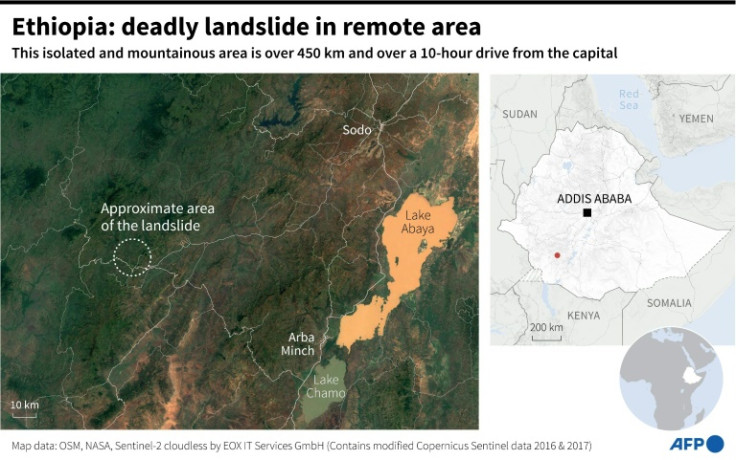
The landslide is the deadliest on record in Ethiopia, Africa’s second most populous nation which is often battered by climate-related disasters.
Officials have said that most of the victims were buried after they rushed to help after the first landslide, which followed heavy rains Sunday in the area roughly 480 kilometres (270 miles) from the capital Addis Ababa — about a 10-hour drive.
In one graphic scene shown in images posted on social media by the local authority, dozens of men surrounded a pit where human limbs were exposed in the mud.
Other villagers carried bodies on makeshift stretchers while in a nearby tent women wailed as they sat near a row of bodies wrapped in shrouds being prepared for burial.
OCHA said 12 people who sustained injuries had been taken to a local hospital, while at least 125 are displaced and sheltering with other local residents.
The number of missing is not known.
UN chief Antonio Guterres sent his condolences over the disaster, with his spokesman Stephane Dujarric saying he was “deeply saddened”.
“The United Nations and its partners are working closely with the Government, evaluating the humanitarian situation to determine the extent of the damage and assess the humanitarian needs of the affected population,” Dujarric said.
“UN agencies are dispatching food, nutrition, health and other critical supplies to help people affected by the landslides.”
Senait Solomon, head of communications for the South Ethiopia regional government, told AFP on Wednesday that the landslide site was sloped and “prone to disasters”, adding that conservation work to protect the area, including tree planting, had been under way at the time of the landslides.
More than 21 million people or about 18 percent of the population rely on humanitarian aid in Ethiopia as a result of conflict and natural disasters such as flooding and drought.
OCHA said earlier this week that that a similar but lower-scale landslide struck in May in the same area, killing more than 50 people.
Seasonal rains in South Ethiopia state between April and early May had caused flooding, mass displacement and damage to livelihoods and infrastructure, it had said in May.
In 2017, at least 113 people died when a mountain of garbage collapsed in a dump in the outskirts of Addis Ababa.
The deadliest landslide in Africa was in Sierra Leone’s capital in Freetown in August 2017, when 1,141 people perished.
Mudslides in the Mount Elgon region of eastern Uganda killed more than 350 people in February 2010.
AFP
AFP







