Rohingya cleric Abdur Rashid still believes children are divine gifts, but life in a Bangladeshi refugee camp with six little mouths to feed has left him and his wife unwilling to accept another heavenly blessing.
Earlier this year, his wife Nosmin asked doctors to fit her with a contraceptive implant, a decision that cultural norms among the persecuted and largely Muslim minority would have rendered unthinkable a few years ago.
But since fleeing a military crackdown in Myanmar five years ago, life in the overcrowded refugee settlements of their reluctant hosts has prompted the couple and many other families to limit the size of their households.
Roughly two-thirds of Rohingya couples are now using some form of birth control — up from virtually none five years ago, according to figures from the UN refugee agency.
“Children are blessings from God and he’s the one who arranges necessities for them — but we have been stuck in this squalid camp for years now,” Rashid told AFP.
“I prefer not to bring in any more life in the face of this hardship.”
Islam takes no uniform view of birth control — a practice endorsed by some Muslim communities and abhorred by others.
A few short years ago, many Rohingya believed birth control was against the tenets of their faith.
That taboo has withered, with Rashid among hundreds of religious leaders within the refugee community delivering sermons in mosques in support of contraceptive use.
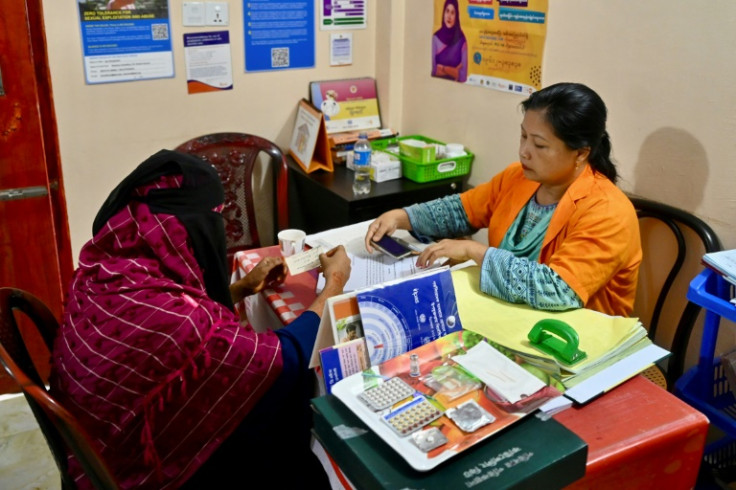
He and others have volunteered for a dedicated public health campaign that aid workers and Bangladeshi authorities say has brought a sweeping change in attitudes towards family planning.
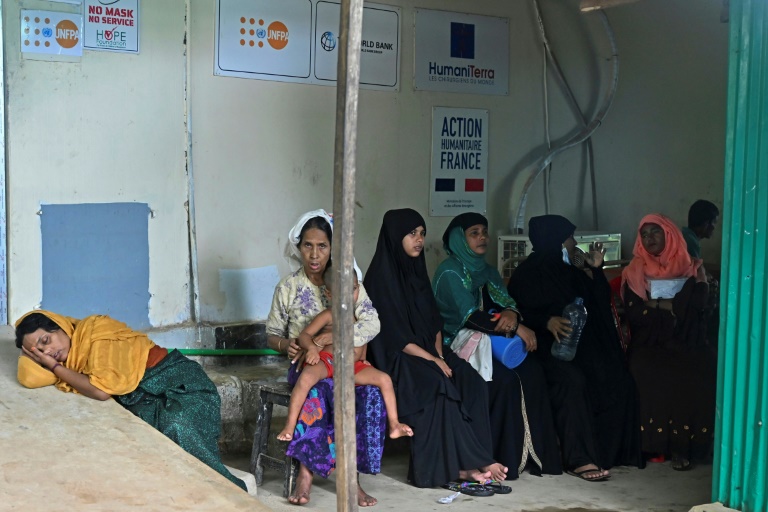
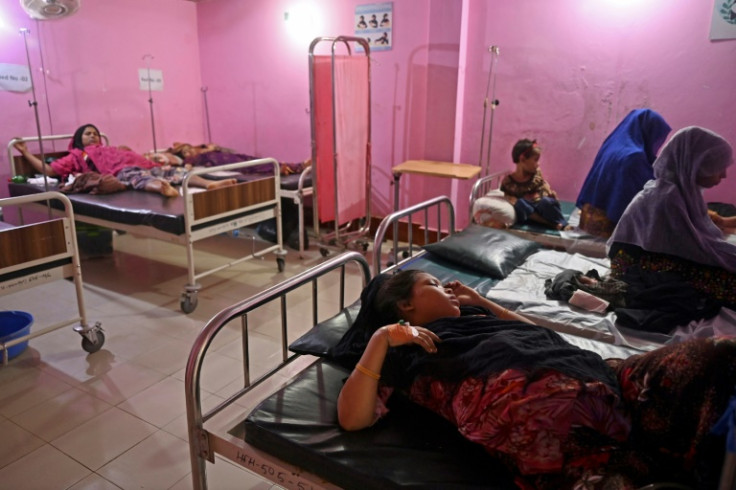
Around 190,000 family planning visits were made in the first six months of the year from among the million or so Rohingya refugees living in the Bangladesh camps, including many women seeking abortions.
“Eventually, I may want one more baby. But not right now,” said mother-of-two Noorjahan Begum, 25.
Begum spoke to AFP after walking through the day to her nearest clinic, carrying her six-month-old son, to ask doctors to terminate her latest pregnancy.
Dependent on humanitarian aid to survive, Begum said she lacked the resources to adequately feed and shelter another baby.
“God willing, I will take permanent birth control measures after my third child,” she added.
Family planning has a fraught history for the Rohingya, about 750,000 of whom fled their homes in Myanmar five years ago after a crackdown by security forces now subject to a UN genocide investigation.
Before that exodus, the Rohingya were subject to decades of discriminatory policies by Myanmar authorities who considered them illegal immigrants from Bangladesh, despite their long-established presence.
Myanmar’s government denied them citizenship and prevented them from moving freely in an effort to confine the population to a remote corner of the country.
It also attempted to forbid Rohingya women from having more than two children and made a written pledge to that effect a condition of issuing marriage licences to Rohingya couples.
Since 2017, Bangladesh has struggled to support its immense refugee population, for whom the prospects of a wholesale return to Myanmar or resettlement elsewhere are vanishingly remote.
Efforts to ease overcrowding in the camps have seen thousands of refugees moved to a flood-prone island — a policy criticised by rights groups, which said many had been relocated against their will.
Bangladesh has also been unnerved by resentment and protests from those living close to the camps, where refugees outnumber the local population two-to-one.
Yet public health experts say the most enthusiastic backers of the family planning campaign have been the refugees themselves.
“When they came here, almost every Rohingya we met had never heard of condoms or birth control pills,” local family planning office chief Pintu Kanti Bhattacharjee told AFP.
“Now they welcome it. They understand too many children can make their lives harder.”






![‘Transformers: Rise Of The Beasts’ Trailer Shows Maximals Vs Predacons Battle [Watch]](https://d.ibtimes.com/en/full/2455673/transformers.jpg)
