AFP
India’s parliament was adjourned twice on Monday after lawmakers held rowdy protests and threw paper at the speaker following the expulsion from the house of top opposition figure Rahul Gandhi.
Gandhi lost his parliamentary seat on Friday after being convicted in a case that critics say shows how the rule of law is under threat in the world’s largest democracy under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
The speaker called off proceedings less than a minute after opposition MPs wearing black erupted in shouting, some of them throwing bits of paper at him.
“I want to run the House with dignity,” Speaker Om Birla said.
The session resumed several hours later only to be abandoned again after about 10 minutes as opposition MPs chanted anti-Modi slogans and waved “Democracy in danger” placards.
It was the latest in a string of stoppages in recent weeks in India’s often raucous parliament among lawmakers representing India’s 1.4 billion people.
Opposition MPs have been demanding a probe into potential links between Modi and the business empire of tycoon Gautam Adani, which has been hit by allegations of accounting fraud.
Debates have also descended into shouting matches over comments made by Gandhi in Britain in early March that Indian democracy is “under attack”.
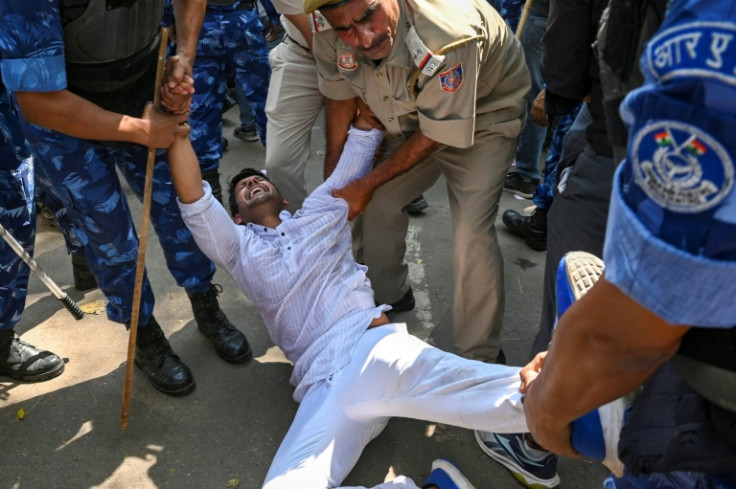
Opposition lawmakers from different parties also staged protests in New Delhi on Monday, the latest in a series of recent demonstrations.
Piyush Goyal, trade minister and a member of Modi’s ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), on Monday accused the opposition of “cheap politics” and “trying to mislead people”.
Gandhi “has no right to consider himself above the law of the country”, Goyal told reporters.
Despite facing criticism from human rights groups, Modi has largely been courted by Western governments which see India, this year’s host of the Group of 20 economies, as a bulwark against China and potential player on the Ukraine war.
“Respect for the rule of law and judicial independence is a cornerstone of any democracy, and we’re watching Mr Gandhi’s case in Indian courts,” US State Department spokesman Vedant Patel said, steering clear of condemning the opposition leader’s expulsion.
“We engage with the government of India on our shared commitment to democratic values, including, of course, freedom of expression,” Patel told reporters in Washington.
Gandhi, 52, is the leading face of the opposition Congress party, once the dominant force of Indian politics, and is the scion of India’s most famous political dynasty.
But Congress has for years been repeatedly crushed in elections by Modi’s BJP and its nationalist appeals to India’s Hindu majority.
The lower house of parliament ruled Gandhi ineligible to sit as an MP on Friday, a day after he was sentenced to two years for defamation. He is appealing.
The conviction stemmed from a remark made during the 2019 election campaign when Gandhi had asked why “all thieves have Modi as (their) common surname”.
His comments were portrayed as a slur against the prime minister and against all those with the same surname, which is associated with the lower rungs of India’s caste hierarchy.
A BJP spokesman said Thursday the court acted with “due judicial process” in arriving at its ruling in the case, one of several Gandhi is facing.
Legal action has been widely deployed against opposition party figures and institutions seen as critical of the Modi government during its nine years in power.
Domestic and international media have also come under growing pressure. Last month, tax inspectors raided the local offices of Britain’s BBC.
The Editors Guild of India said the raids demonstrated a “trend of using government agencies to intimidate or harass press organisations that are critical of government policies”.
On Saturday, Gandhi, who recently completed a walk across India that was hailed as a success by commentators, said he would “do whatever I have to do to defend the democratic nature of this country”.

AFP